Impala JDBC 动态设置查询选项
前篇文章 Impala 设置查询选项 介绍常用设置查询选项的方法,本文详细介绍实现动态查询选项过程。
AOP 概念
在我们开始之前,让我们对术语和核心概念做一个回顾:
- Aspect:切面,由切点和增强相结合而成,定义增强应用到哪些切点上。即一个横跨多个核心逻辑的功能,或者称之为系统关注点。
- Joinpoint:连接点,这是程序执行过程中的一个特殊点,例如方法执行,构造函数调用或字段分配。
- Pointcut:切入点,一个匹配连接点的正则表达式。 每当任何连接点匹配一个切入点时,就执行与该切入点相关联的指定增强。
- Advice:增强,指特定连接点上执行的动作,实际中想要添加的功能,如日志、权限校验。有5种:
@Before @After @AfterReturning @AfterThrowing @Around。 - Weaving:织入,即对方法的增强,将切面的代码织入(应用)到目标函数的过程。
Spring AOP 和 AspectJ
下表总结了 Spring AOP 和 AspectJ 之间的关键区别:
| Spring AOP | AspectJ |
|---|---|
| 在纯 Java 中实现 | 使用 Java 编程语言的扩展实现 |
| 不需要单独的编译过程 | 除非设置 LTW,否则需要 AspectJ 编译器 (ajc) |
| 只能使用运行时织入 | 运行时织入不可用。支持编译时、编译后和加载时织入 |
| 功能不强-仅支持方法级编织 | 更强大 - 可以编织字段、方法、构造函数、静态初始值设定项、最终类/方法等……。 |
| 只能在由 Spring 容器管理的 bean 上实现 | 可以在所有域对象上实现 |
| 仅支持方法执行切入点 | 支持所有切入点 |
| 代理是由目标对象创建的, 并且切面应用在这些代理上 | 在执行应用程序之前 (在运行时) 前, 各方面直接在代码中进行织入 |
| 比 AspectJ 慢多了 | 更好的性能 |
| 易于学习和应用 | 相对于 Spring AOP 来说更复杂 |
选择正确的框架
选择那个框架很大程度上取决于我们的要求:
- 框架: 如果应用程序没有使用 Spring 框架, 那么我们就别无选择, 只能放弃使用 Spring AOP 的想法, 因为它无法管理任何超出 Spring 容器范围的东西。但是, 如果我们的应用程序是完全使用 Spring 框架创建的, 那么我们可以使用 Spring AOP, 因为它是简单的学习和应用。
- 灵活性: 由于有限的 joinpoint 支持, Spring AOP 不是一个完整的 AOP 解决方案, 但它解决了程序员面临的最常见的问题。尽管如果我们想深入挖掘和开发 AOP 以达到其最大能力, 并希望得到广泛的可用 joinpoints 的支持, 那么最好选择 AspectJ。
- 性能: 如果我们使用的是有限的切面, 那么就会有细微的性能差异。但有时, 应用程序有成千上万个切面的情况。我们不想在这样的情况下使用运行时编织, 所以最好选择 AspectJ。AspectJ 已知的速度比 Spring AOP 快8到35倍。
- 两者的最佳之处: 这两个框架都是完全兼容的。我们总是可以利用 Spring AOP;只要有可能, 仍然可以在不支持前者的地方使用 AspectJ 获得支持。
基于我们的需求:对 Impala jdbc 驱动包的内容做增强。不受 Spring 管理,AspectJ 支持这种方式,并提供了 Compile-time weaving,Post-compile weaving ,Load-time weaving 三种织入方式,从开发部署便捷性上这里选择 Post-compile weaving 方式。
环境
Spring Boot: 2.1.4.RELEASE
Impala JDBC: 2.6.17.1020
步骤:
步骤中省略了数据源的配置过程。驱动可以开启日志,有利于我们跟踪分析请求。
1
jdbc:impala://localhost:21050;LogLevel=6;LogPath=/tmp/impala
1. 添加 aspects 支持
首先,我们通过 Maven 引入Spring 对 aspects 的支持:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
<!-- aspects -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>${aspectj.version}</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
上述依赖会自动引入 AspectJ,使用 AspectJ 实现 AOP 比较方便。
2. 定义切面类
然后,我们定义一个HS2ClientAspect:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
package com.cloudera.example.aspects;
import com.cloudera.example.helper.HS2ClientHelper;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* HS2ClientWrapper 类的切面。
* <p>
*/
@Aspect
public class HS2ClientAspect {
private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
/**
* 切入点,一个匹配连接点的正则表达式。
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.cloudera.impala.hivecommon.api.HS2ClientWrapper" +
".ExecuteStatement(..))")
public void hs2Pointcut() {
// Method is empty as this is just a Pointcut, the implementations are in the advices.
}
/**
* 前置增强,目标方法执行前之前执行。
*
* @param joinPoint 连接点
*/
@Before("hs2Pointcut()")
public void optimizeQueryOption(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Enter: {}.{}() with argument[s] = {}",
joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(),
joinPoint.getSignature().getName(), Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
// 执行前,设置查询选项
HS2ClientHelper.getInstance().addQueryOption(joinPoint.getSignature().getName(),
joinPoint.getArgs());
}
}
观察hs2Pointcut() 方法,定义了一个@Pointcut注解,后面的字符串是告诉 AspectJ 应该如何匹配一个切入点,注意这步可以省略,可以字符串直接写在Advice上,如果只有一个 Advice 可以使用这种方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
@Before("execution(public * com.cloudera.impala.hivecommon.api.HS2ClientWrapper" +
".ExecuteStatement(..))")
public void optimizeQueryOption(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// ....
}
观察optimizeQueryOption()方法,我们定义了一个@Before注解,后面的字符串(这里也可以直接写匹配表达式)是告诉 AspectJ 应该在何处执行该方法,这里的意思是:执行HS2ClientWrapper的ExecuteStatement方法前执行optimizeQueryOption()代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
/**
* 添加优化查询选项参数
*
* @param req ExecuteStatementReq
*/
public void addOptimizeQueryOption(TExecuteStatementReq req) {
// 1. 获得请求的查询配置属性
Map<String, String> confOverlay = req.getConfOverlay();
if (null == confOverlay) {
confOverlay = Maps.newHashMap();
req.setConfOverlay(confOverlay);
}
// 2. 获得sql语句的唯一标识
byte[] guid = req.getSessionHandle().getSessionId().getGuid();
String sessionId = StringHelper.getGuid(guid);
// a. 从 sql 语句提取 traceId(可能取不到,驱动会对 sql 自动翻译)
String statement = req.getStatement();
String traceId = SQLHelper.getTraceIdBySql(statement);
// b. 获取当前 session 的优化参数 Map<sessionId, traceId>
if (StringUtils.isBlank(traceId)) {
traceId = sessionId;
}
// 3. 获取查询选项并配置
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(traceId)) {
Map<String, String> queryOptions = SQLHelper.getConfByTraceId(traceId);
if (null != queryOptions) {
confOverlay.putAll(queryOptions);
}
}
log.info("Optimize query option: sessionid={}, statement={}, confOverlay={}", sessionId,
statement, confOverlay);
}
3. 添加 aspects 编译插件
紧接着,添加 aspectj 插件用于织入代码。aspectj 插件是支持 jar 和 .class 做织入的。这里未使用的原因是驱动包太复杂织入失败,实际上我们仅需要对一类做织入 ,通过maven-dependency-plugin插件配合自动完成编译后织入。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
<!-- Unzip the classes to be woven from the JAR and do so before compiling -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-dependency-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>unpack</id>
<phase>generate-sources</phase>
<goals>
<goal>unpack</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<artifactItems>
<artifactItem>
<groupId>Impala</groupId>
<artifactId>ImpalaJDBC${jdbc.version}</artifactId>
<version>${impala.jdbc.version}</version>
<type>jar</type>
<!-- 要织入的类 -->
<includes>com/cloudera/impala/hivecommon/api/HS2ClientWrapper*.*</includes>
<outputDirectory>${project.build.directory}/unwoven-classes</outputDirectory>
</artifactItem>
</artifactItems>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectj-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.11</version>
<configuration>
<complianceLevel>1.8</complianceLevel>
<verbose>true</verbose>
<!-- Weaving already compiled classes -->
<weaveDirectories>
<weaveDirectory>${project.build.directory}/unwoven-classes</weaveDirectory>
</weaveDirectories>
<aspectLibraries>
<aspectLibrary>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
</aspectLibrary>
</aspectLibraries>
</configuration>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjtools</artifactId>
<version>${aspectj.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>${aspectj.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<executions>
<execution>
<!-- Compile and weave aspects after all classes compiled by javac -->
<!-- <phase>process-classes</phase>-->
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
<goal>test-compile</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
执行编译:mvn clean compile 或者点击 IDE 中 maven 插件的 compole。
编译后classes应该有这个类,这是织入之后的类,
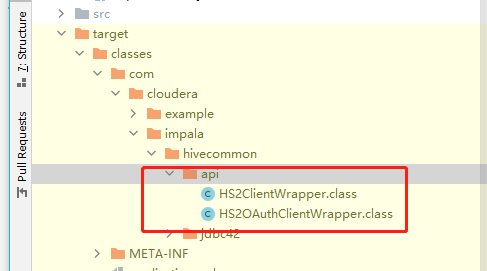
反编译后找到ExecuteStatement方法,可以看到前两行是织入的代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public TExecuteStatementResp ExecuteStatement(TExecuteStatementReq arg0) throws TException {
JoinPoint var3 = Factory.makeJP(ajc$tjp_0, this, this, arg0);
HS2ClientAspect.aspectOf().optimizeQueryOption(var3);
LogUtilities.logFunctionEntrance(this.m_logger, new Object[]{arg0});
HS2ClientWrapper.TCLIFunction var2 = new HS2ClientWrapper.TCLIFunction() {
public TExecuteStatementResp clientCall(Object var1, HS2ClientWrapper var2) throws TException {
TExecuteStatementResp var3 = var2.callExecuteStatement((TExecuteStatementReq)var1);
return var3;
}
};
return (TExecuteStatementResp)this.executeWithRetry(var2, arg0, this);
}
4. 测试
最后测试类,可以通过发送set语句验证是否生效。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
package com.cloudera.example.mapper;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import com.cloudera.example.ImpalaJdbcExampleApplicationTests;
import com.cloudera.example.helper.SQLHelper;
import com.google.common.collect.Maps;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class ImpalaQueryOptionsTest extends ImpalaJdbcExampleApplicationTests {
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
public void testQueryOptions() {
// 1. 先把查询选项放到缓存。
// 2. 发送 set 请求,获得当前查询选项
// 3. aspectj 拦截 ExecuteStatement 方法设置查询选项参数 confOverlay
// 4. 验证结果,从中取出设置的查询选项做判断
// 1. 设置查询选项
Map<String, String> queryOptions = Maps.newHashMap();
queryOptions.put("request_pool", "mypool");
queryOptions.put("mt_dop", "2");
String sqlStatement = "/* id:1 */ set";
String sessionId = null;
Connection con = null;
try {
con = dataSource.getConnection();
// 设置查询选项
SQLHelper.setSqlConf("1", queryOptions);
// 当前session也设置一下
sessionId = SQLHelper.getSessionId(con);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(sessionId)) {
SQLHelper.setSqlConf(sessionId, queryOptions);
}
// 2. 发送查询请求
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sqlStatement);
System.out.println("\n== Begin Query Results ======================");
Map<String, String> result = Maps.newHashMap();
// print the results to the console
while (rs.next()) {
String option = rs.getString(1);
String value = rs.getString(2);
result.put(option, value);
}
System.out.println("result: " + result);
System.out.println("== End Query Results =======================\n\n");
// 4. 验证,从返回结果里获取配置的查询选项并比较
queryOptions.forEach((k, v) -> {
String actual = result.get(k.toUpperCase());
assertEquals("failure - strings are not equal", v, actual);
});
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
SQLHelper.clearByTraceId(sessionId);
try {
con.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// swallow
}
}
}
}
日志里会有这条记录,如果没有请检查是否漏掉了编译,IDE 不会使用我们配置的插件编译。
//tmp/impala/Impala_connection_0.log:
1
TRACE 1 com.cloudera.impala.hivecommon.api.HS2ClientWrapper.ExecuteStatement(TExecuteStatementReq(sessionHandle:TSessionHandle(sessionId:THandleIdentifier(guid:DC 4C D9 5A 49 81 45 4D A8 0D 7C D9 11 3B E7 3A, secret:0E DD 99 AE FF 4E 42 60 96 27 9D 10 A1 20 B2 91)), statement:set, confOverlay:{request_pool=mypool, mt_dop=2}, runAsync:true)): +++++ enter +++++
注意看confOverlay的值。
小结
本文先介绍了 AOP 及 Aspect 相关知识,接着介绍动态查询选项的工程实现。
参考:

留下评论